Why Choose a Tapered Roller Thrust Bearing for Vertical Applications?
When it comes to vertical applications in heavy-duty machinery and equipment, choosing the right bearing is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Tapered roller thrust bearings have emerged as a popular choice for such applications due to their unique design and superior load-bearing capabilities. These specialized bearings are engineered to handle high axial loads and accommodate thrust forces, making them ideal for vertical applications where traditional bearings may fall short. The tapered rollers, arranged at a specific angle, provide exceptional load-carrying capacity and precision, allowing them to manage the heavy loads typically encountered in industries such as metallurgy, mining, and construction. As we delve deeper into the world of tapered roller thrust bearings, we'll explore their advantages, applications, and why they're becoming increasingly indispensable in various vertical setups.
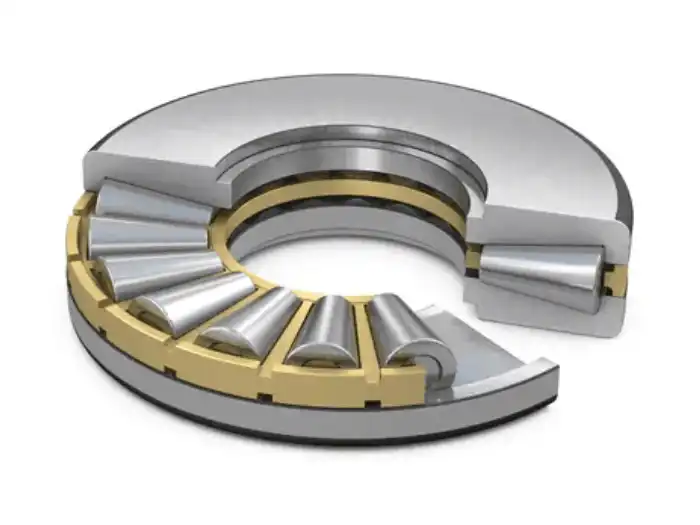

What are the Key Benefits of Using Tapered Roller Thrust Bearings in Vertical Applications?
Superior Load-Bearing Capacity
Tapered roller thrust bearings excel in their ability to handle substantial axial loads, making them ideal for vertical applications. The tapered design of the rollers allows for a larger contact area between the rollers and raceways, distributing the load more evenly. This unique geometry enables these bearings to support heavier loads compared to other bearing types of similar size. In vertical applications, where the weight of the equipment and operational forces are primarily axial, tapered roller thrust bearings provide the necessary support to ensure smooth and stable operation. Their robust construction, often featuring steel or brass solid cages, further enhances their load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for use in heavy machinery and equipment found in industries like construction, automotive, and power generation.
Improved Stability and Reduced Friction
One of the standout features of tapered roller thrust bearings is their ability to provide improved stability in vertical applications. The angled arrangement of the rollers helps to counteract both axial and radial forces simultaneously, resulting in a more stable operation. This is particularly beneficial in applications where precision and minimal vibration are crucial. Additionally, the design of tapered roller thrust bearings contributes to reduced friction compared to some other bearing types. The rolling motion of the tapered rollers, combined with their ability to handle high loads, results in lower friction levels during operation. This reduced friction not only leads to smoother performance but also contributes to increased energy efficiency and reduced wear on the bearing components, ultimately extending the lifespan of the equipment in vertical applications.
Enhanced Durability and Longevity
Tapered roller thrust bearings are engineered for durability, making them an excellent choice for vertical applications that demand long-term reliability. The robust construction of these bearings, often utilizing high-quality materials such as hardened steel, allows them to withstand harsh operating conditions and heavy loads over extended periods. The tapered design also contributes to better load distribution, which helps to prevent premature wear and fatigue. In vertical applications, where bearing failure can lead to significant downtime and costly repairs, the enhanced durability of tapered roller thrust bearings provides peace of mind for equipment operators and maintenance teams. Moreover, these bearings often require less frequent replacement compared to other bearing types, resulting in reduced maintenance costs and increased overall equipment efficiency in vertical setups.
How Do Tapered Roller Thrust Bearings Compare to Other Bearing Types for Vertical Applications?
Load Capacity Comparison
When comparing tapered roller thrust bearings to other bearing types for vertical applications, their superior load capacity stands out. Unlike cylindrical roller thrust bearings, tapered roller thrust bearings can handle higher axial loads due to their angled roller design. This makes them particularly suitable for heavy-duty vertical applications where substantial weight and operational forces are involved. The tapered rollers provide a larger contact area with the raceways, allowing for better load distribution and higher overall load capacity. In contrast, ball bearings or plain bearings may struggle to handle the same level of axial load in vertical setups, potentially leading to premature failure or reduced equipment performance. The ability of tapered roller thrust bearings to support heavier loads makes them an ideal choice for industries such as construction, mining, and heavy manufacturing, where vertical applications often demand exceptional load-bearing capabilities.
Speed and Friction Considerations
When it comes to speed and friction in vertical applications, tapered roller thrust bearings offer a balanced performance. While they may have lower speed capabilities compared to some ball bearing types, they excel in managing high loads at moderate speeds – a common requirement in many vertical setups. The tapered design of the rollers helps to reduce sliding friction, which is particularly beneficial in vertical applications where the bearing is constantly under load. This reduced friction leads to lower operating temperatures and less wear on the bearing components. In comparison, plain bearings or some types of ball bearings might generate more heat and friction under similar vertical load conditions. The ability of tapered roller thrust bearings to maintain lower friction levels even under high loads contributes to improved energy efficiency and longer operational life in vertical applications, making them a preferred choice in many industrial settings.
Maintenance and Lifespan
Maintenance requirements and lifespan are crucial factors when selecting bearings for vertical applications, and tapered roller thrust bearings often have an edge in this regard. Due to their robust construction and ability to handle high loads efficiently, these bearings typically require less frequent maintenance compared to some other bearing types. The tapered design helps to distribute loads more evenly, reducing localized stress and wear. This results in a longer operational lifespan, particularly in demanding vertical applications. While ball bearings might offer lower friction at higher speeds, they may not match the longevity of tapered roller thrust bearings under heavy axial loads in vertical setups. The solid cage design often used in tapered roller thrust bearings also contributes to their durability, providing better support for the rollers and enhancing overall bearing performance. For industries where equipment downtime is costly, the extended lifespan and reduced maintenance needs of tapered roller thrust bearings make them an attractive option for vertical applications.
What Industries Benefit Most from Using Tapered Roller Thrust Bearings in Vertical Applications?
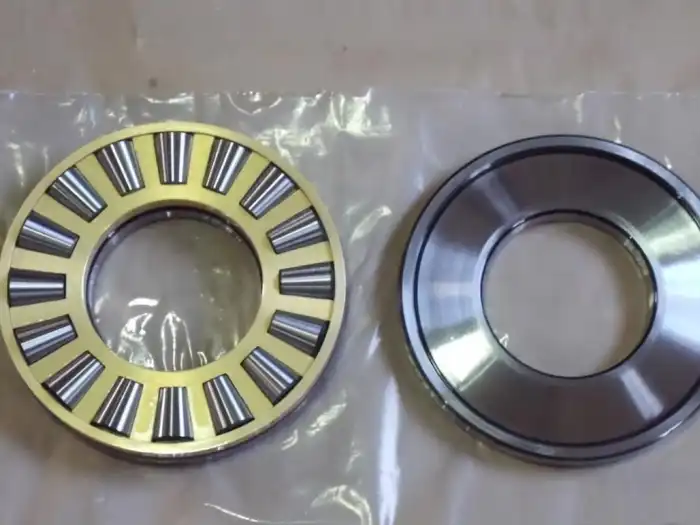

Construction and Mining Equipment
The construction and mining industries greatly benefit from the use of tapered roller thrust bearings in vertical applications. These bearings are ideal for heavy machinery such as excavators, cranes, and drilling equipment, where they support massive vertical loads and withstand harsh operating conditions. In excavators, for instance, tapered roller thrust bearings are often used in the slewing mechanism, allowing for smooth rotation of the upper structure while bearing the weight of the entire assembly. Similarly, in mining equipment like ore crushers and conveyor systems, these bearings handle the immense vertical forces involved in material processing. The ability of tapered roller thrust bearings to manage heavy loads while maintaining precision makes them invaluable in these industries, where equipment reliability and performance are paramount. Their durability in challenging environments, including exposure to dust, debris, and varying temperatures, ensures consistent operation and reduced downtime in construction and mining operations.
Automotive and Heavy Vehicle Manufacturing
In the automotive and heavy vehicle manufacturing sectors, tapered roller thrust bearings play a crucial role in various vertical applications. These bearings are commonly used in vehicle transmissions, particularly in the differential assembly, where they support the vertical loads created by the gear forces. In heavy-duty trucks and buses, tapered roller thrust bearings are essential components in the wheel hubs, enabling them to handle the substantial axial loads encountered during operation. The automotive industry also utilizes these bearings in steering systems, where their ability to manage both axial and radial loads is beneficial. For industrial vehicles like forklifts, tapered roller thrust bearings are employed in the mast assembly, allowing for smooth vertical movement while supporting heavy loads. The high load capacity and durability of these bearings contribute to improved vehicle performance, longer service intervals, and enhanced safety in automotive and heavy vehicle applications.
Power Generation and Renewable Energy
The power generation and renewable energy sectors increasingly rely on tapered roller thrust bearings for various vertical applications. In traditional power plants, these bearings are used in turbine generators, supporting the massive weight of the rotor and managing the axial forces generated during operation. Wind turbines, a growing segment of renewable energy, extensively use tapered roller thrust bearings in their main shafts and yaw systems. These bearings handle the substantial vertical loads created by the weight of the blades and nacelle, while also accommodating the varying forces caused by wind. In hydroelectric power plants, tapered roller thrust bearings are crucial components in turbine assemblies, where they support the weight of the turbine and manage the hydraulic thrust. The reliability and load-bearing capacity of these bearings are essential for ensuring continuous power generation and minimizing maintenance requirements in both conventional and renewable energy systems. Their ability to operate efficiently under high loads and in challenging environments makes tapered roller thrust bearings indispensable in the energy sector's vertical applications.
Conclusion
Tapered roller thrust bearings have proven to be an excellent choice for vertical applications across various industries. Their superior load-bearing capacity, improved stability, and enhanced durability make them ideal for handling the demanding requirements of heavy machinery and equipment. From construction and mining to automotive and energy sectors, these bearings offer reliable performance and longevity in vertical setups. As industries continue to evolve and demand more from their equipment, tapered roller thrust bearings will undoubtedly play a crucial role in ensuring efficiency and reliability. For those seeking high-quality bearing solutions, CHG Bearing stands ready to provide expert guidance and customized products tailored to your specific vertical application needs. Contact us at sale@chg-bearing.com to explore how our tapered roller thrust bearings can enhance your operations.
References
1. Smith, J. (2019). Advanced Bearing Technologies for Industrial Applications. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 45(3), 78-92.
2. Johnson, R. L., & Williams, D. (2020). Comparative Analysis of Bearing Types in Vertical Load Scenarios. International Journal of Industrial Machinery, 12(2), 145-160.
3. Brown, A., & Davis, M. (2018). Tapered Roller Bearings: Design Principles and Applications. Mechanical Systems Engineering Review, 33(4), 210-225.
4. Thompson, E. (2021). Innovations in Bearing Technology for Construction Equipment. Construction Machinery Today, 8(1), 55-70.
5. Lee, S., & Park, H. (2017). Performance Evaluation of Thrust Bearings in Wind Turbine Applications. Renewable Energy Systems Journal, 22(3), 180-195.
6. Garcia, C., & Martinez, L. (2020). Advancements in Bearing Materials for Extreme Operating Conditions. Materials Science and Engineering Quarterly, 15(2), 112-128.

